Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Transforming Reality
Introduction: In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one tool stands out as a true game-changer in the realms of design and innovation – Computer-Aided Design, commonly...

Introduction:
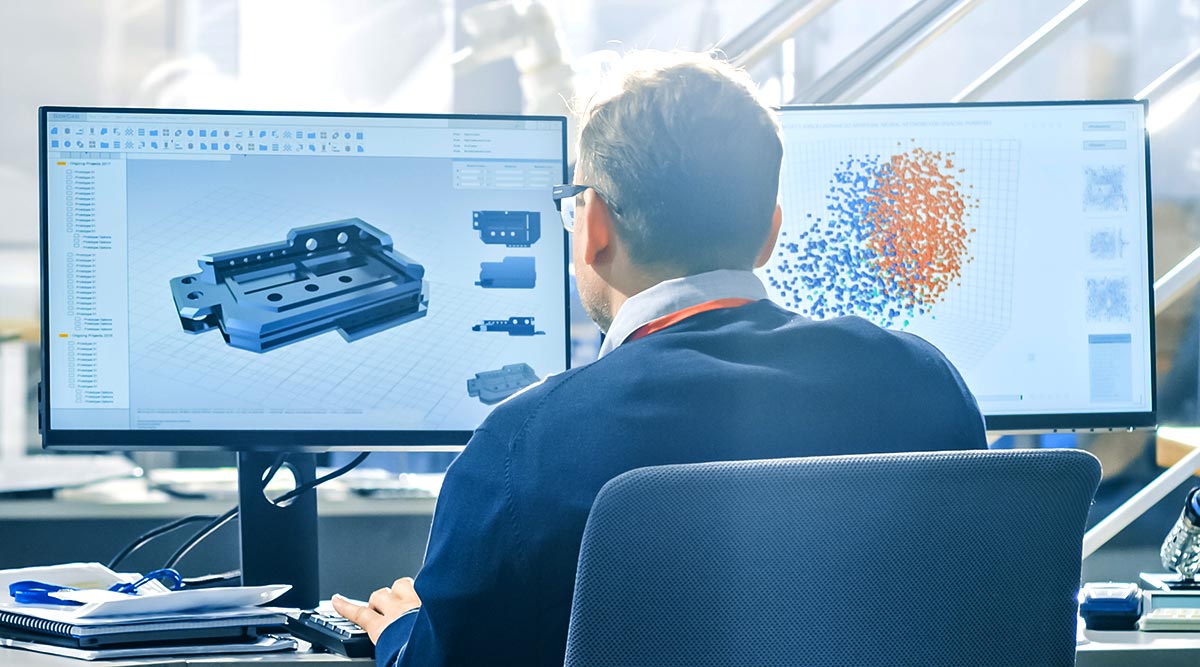
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one tool stands out as a true game-changer in the realms of design and innovation – Computer-Aided Design, commonly known as CAD. This revolutionary technology has not only transformed the way we conceptualise and create designs but has also become an integral part of various industries, ranging from architecture and engineering to product design and manufacturing. Let’s delve into the world of Computer-Aided Design and explore its origins, evolution, and its profound impact on the way we bring ideas to life.
What is Computer-Aided Design (CAD)?
Computer-Aided Design, or CAD, refers to the use of computer technology to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimisation of designs. Unlike traditional drafting methods that relied on manual drawings and physical prototypes, CAD enables designers and engineers to create precise, digital representations of their ideas. These digital models serve as a virtual blueprint, allowing for efficient visualisation, analysis, and modification of designs before they are brought into the physical realm.
Origins and Evolution of Computer-Aided Design
The roots of CAD can be traced back to the early 1960s when computer technology was in its infancy. The first CAD systems were primarily used for aerospace and automotive design, aiming to streamline the design and manufacturing processes. As technology advanced, CAD systems evolved from simple 2D drafting tools to sophisticated 3D modelling environments.
The 1980s marked a significant milestone in CAD history with the development of commercial CAD software. Companies like AutoCAD emerged, introducing accessible and user-friendly CAD solutions to a broader audience. This democratisation of CAD technology paved the way for its widespread adoption across diverse industries.
Key Components of Computer-Aided Design
- Geometric Modelling: CAD systems enable the creation of digital models by defining shapes and dimensions in a virtual environment. Geometric modelling serves as the foundation for all design work, allowing users to build and manipulate objects with precision.
- Rendering and Visualisation: CAD software provides realistic rendering capabilities, allowing designers to visualise their creations in lifelike detail. This aids in communication and decision-making processes by offering a clear representation of the final product.
- Parametric Design: One of the distinguishing features of CAD is its parametric design capabilities. This means that changes to one aspect of a design automatically update related elements, ensuring consistency and reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Simulation and Analysis: CAD tools facilitate the simulation and analysis of designs, enabling engineers to assess factors such as structural integrity, thermal performance, and fluid dynamics. This helps identify potential issues early in the design process, minimising costly revisions.
Where is Computer-Aided Design used
CAD has become an indispensable tool across various industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities.

- Architecture: Architects use CAD to create detailed building plans, visualise designs in 3D, and simulate how structures will interact with their surroundings.
- Engineering: In engineering disciplines, CAD is employed for designing machinery, electrical systems, and infrastructure projects. It plays a crucial role in prototyping and testing components before physical production.
- Product Design: CAD is extensively used in product design, allowing designers to create and refine prototypes digitally. This accelerates the product development cycle and reduces the time and cost associated with physical prototyping.
- Manufacturing: CAD plays a pivotal role in computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), where digital designs are translated into instructions for automated production processes such as CNC machining and 3D printing.
- Graphic Design and Animation: CAD tools find applications in graphic design and animation, enabling artists to create intricate visualisations and animations for various media.
Challenges and Future Trends
While CAD has revolutionised design processes, it is not without its challenges. The complexity of some CAD software can pose a steep learning curve for beginners, and interoperability issues between different CAD systems can hinder collaboration.
Looking ahead, the future of CAD is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and cloud computing. Integration with AI algorithms could automate routine design tasks, while virtual reality interfaces may provide more immersive and intuitive design experiences. Cloud-based CAD solutions offer the potential for enhanced collaboration, enabling teams to work seamlessly across geographical boundaries.
Conclusion
It’s evident that Computer-Aided design has become an indispensable tool for designers, engineers, and innovators across the globe. From transforming the way we conceptualise designs to optimising manufacturing processes, CAD continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible. As we look to the future, the evolution of CAD holds the promise of even more accessible, intelligent, and collaborative design solutions, fueling creativity and innovation for years to come.