What’s the Difference Between BIM and a Digital Twin?
Introduction As digital technologies continue to transform industries, the terms BIM (building information modeling) and Digital Twin are becoming increasingly common. Both co...
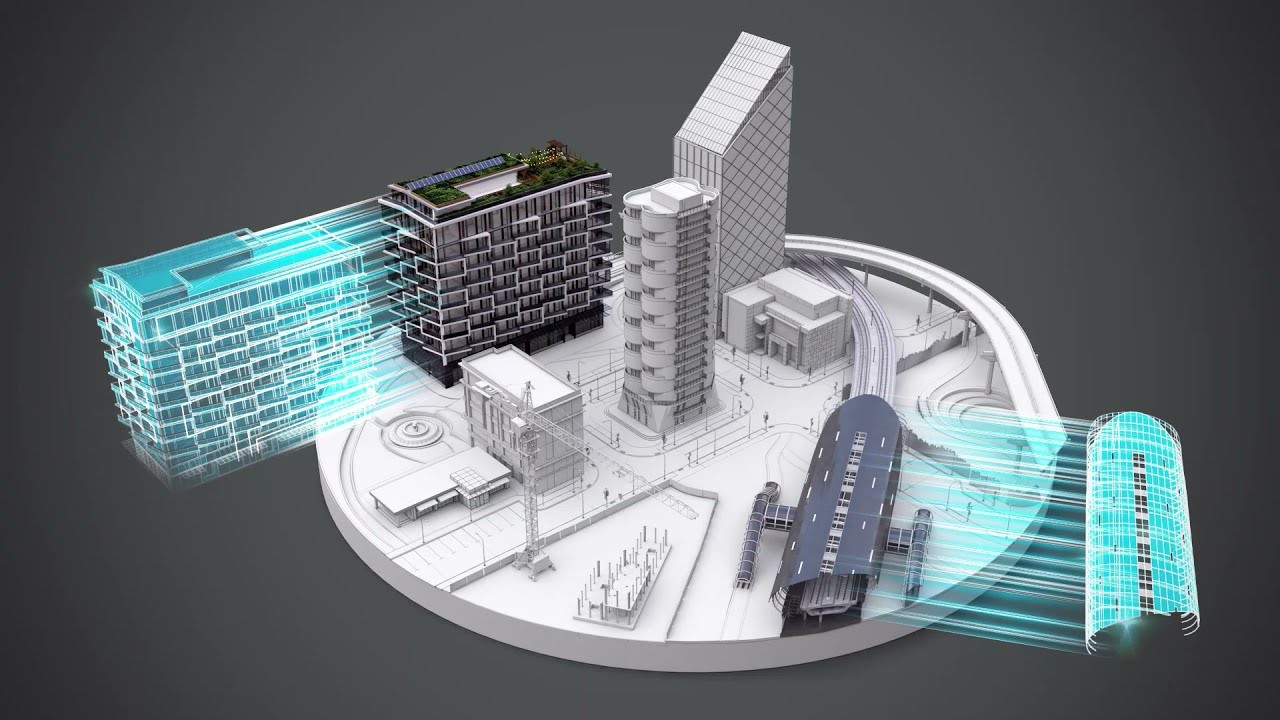

Introduction
As digital technologies continue to transform industries, the terms BIM (building information modeling) and Digital Twin are becoming increasingly common. Both concepts are changing our approaches to design, construction, and asset management, but they are often misunderstood or used interchangeably. In fact, despite certain similarities between BIM and Digital Twin technologies, they serve different purposes and operate at different stages of the project lifecycle.
Let’s explore what each means, how BIM and a Digital Twin differ, and why both are important for modern engineering and construction projects.
Understanding BIM: The Foundation of Digital Design
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a process that involves creating and managing digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. BIM integrates 3D modeling with rich information for planning, design, construction, and documentation.
Simply put, BIM acts as a digital prototype – a detailed virtual model that shows how a facility will look and function before it’s built.
Key Features of BIM:
- 3D Visualization: Provides an accurate geometric representation of structures and components.
- Collaboration: Engineers, architects, and contractors can work on a common model, reducing misunderstandings.
- Data Integration: Each element of the model contains data such as materials, cost, and performance characteristics.
- Lifecycle Management: While BIM is primarily used during the design and construction phases, it can also be used for facility management.
Example:
An engineering team designing a plant might use BIM to model structural layouts, optimize materials, and predict clashes between mechanical and electrical systems before construction begins.
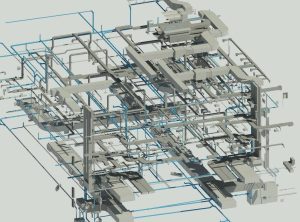
Understanding Digital Twin: The Dynamic Counterpart
A Digital Twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system that operates in real time and is driven by data. Unlike BIM, which is largely static, a Digital Twin continuously evolves, receiving real-time data from sensors and IoT devices installed on the physical asset.
This technology enables real-time monitoring, performance analysis, and predictive maintenance. Essentially, a Digital Twin bridges the gap between the digital model and the physical world.
Key Features of a Digital Twin:
- Real-time data: Integrates real-time data from sensors, equipment, and control systems.
- Behavior modeling: Predicts future states using analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Performance optimization: Helps improve efficiency, detect faults, and optimize maintenance schedules.
- End-to-end lifecycle management: Supports asset performance from design to decommissioning.
Example:
Once a plant is commissioned, a Digital Twin can track equipment performance, energy consumption, and environmental conditions. Engineers can use this data to prevent equipment failures, improve productivity, and effectively plan upgrades.

BIM vs. Digital Twin: The Key Differences
| Aspect | BIM | Digital Twin |
| Purpose | Design, documentation, and construction planning | Real-time operation, monitoring, and optimization |
| Stage of Use | Mainly during design and construction | During operation and maintenance |
| Data Type | Static or historical | Dynamic and continuously updated |
| Connectivity | Limited integration with live systems | Connected to IoT, sensors, and analytics platforms |
| Output | Predictive models and project documentation | Real-time insights, simulations, and decision support |
| Focus | “What will be built” | “How it performs now and in the future” |
How BIM and Digital Twins Work Together
While BIM and Digital Twin differ, they complement each other perfectly. BIM often serves as the starting point for creating a Digital Twin. A BIM model provides a comprehensive digital foundation containing structural, architectural, and system data.
After a facility is built, this model can be overlaid with real-time sensor data from operations, turning it into a fully functional Digital Twin.
This combination offers significant benefits:
- Smooth transition from construction to operations
- Improved asset management and maintenance
- Data-driven decision making throughout the facility’s lifecycle
- Reduced operating costs and downtime
In industries such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and infrastructure, this synergy enables continuous optimization, transforming static projects into intelligent, self-improving systems.
Why Businesses Should Care
The implementation of BIM and Digital Twin technologies is not just a trend, but a strategic step toward digital transformation.
For construction companies, BIM improves project delivery, accuracy, and collaboration.
For facility managers and operators, Digital Twin enhances efficiency, sustainability, and predictive maintenance.
For manufacturers and industrial companies, the integration of these technologies provides end-to-end transparency – from design to operation.
At InStandart, we recognize the value of both approaches. Our team helps companies integrate CAD, BIM, and digital twin technologies to create intelligent, scalable, and efficient solutions. Whether you’re designing a product, a plant, or an industrial system, these digital tools will provide clarity, control, and innovation at every stage.

Conclusion
BIM and Digital Twin technologies are not competitors – they are parts of the same digital ecosystem. BIM lays the foundation by capturing a project’s design intent, while the Digital Twin takes that model into the real world, bringing it to life through data.
Together, they empower organizations to build smarter, manage better, and innovate faster.
As industries evolve toward more connected and sustainable practices, companies that embrace both technologies will lead the way in efficiency, safety, and long-term value creation.