Future of Super Apps: A Trend or a Necessity?
Introduction Super apps, once a regional phenomenon rooted in Asia, have evolved into a global paradigm shift in mobile application development. These platforms consolidate mu...

Introduction
Super apps, once a regional phenomenon rooted in Asia, have evolved into a global paradigm shift in mobile application development. These platforms consolidate multiple services – messaging, payments, e-commerce, ride-hailing, and more – into a single ecosystem. While their popularity has exploded in Asia, especially in countries like China and Indonesia, Western markets have remained fragmented and cautious. However, with shifting consumer behaviors, rising app fatigue, and increasing demand for digital convenience, the question remains: Are super apps merely a trend, or are they becoming a digital necessity?
This whitepaper explores the evolution, market drivers, adoption patterns, future outlook, and strategic considerations surrounding super apps, offering insights for tech companies, digital product leaders, and enterprise strategists.
What is a Super App?
As the digital economy matures, users increasingly expect seamless experiences and integrated services. Super apps have emerged as a one-stop shop, consolidating functionalities that would otherwise require multiple apps. They are redefining how users interact with technology and are becoming central to digital transformation across sectors.
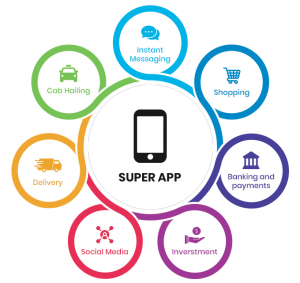
A super app is an all-in-one mobile application platform that offers a variety of services within a single interface. These services typically include:
- Instant messaging
- Payments and digital wallets
- Transportation and delivery services
- E-commerce
- Financial services (loans, insurance, investments)
- Healthcare consultations
- Social media and content platforms
Super Apps in Asia & Global Expansion
The super app phenomenon began in Asia due to unique market conditions:
- WeChat (China): 1.3+ billion monthly users.
- Grab (Southeast Asia): 180 million users across 8 countries.
- GoTo (Indonesia): Result of Gojek and Tokopedia merger.
Why Asia First?
- High mobile penetration but lower desktop access.
- Fragmented digital ecosystems in emerging markets.
- Mobile-first consumers in need of efficient, low-bandwidth solutions.
- Digital payments leapfrogged traditional banking.
Stat: As of 2024, WeChat facilitates over 1 billion transactions per day.
While super apps dominate Asian markets, Western economies have been slower to adopt them. Key reasons include:
- Strict data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR).
- Established digital infrastructure.
- Consumer resistance to platform monopolies.
- App-store economics and competition rules.
However, cracks are beginning to show in the status quo. Meta (Facebook), PayPal, Amazon, and Elon Musk’s vision for X (formerly Twitter) suggest Western players are eyeing the super app opportunity.

Key Features and Architecture
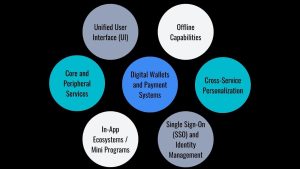
Super apps are complex, multi-layered platforms designed for scalability, modularity, and seamless user interaction. Here’s a breakdown of their defining features and the technical architecture that powers them.
- Unified User Interface (UI). A central dashboard or home screen offers access to all internal and partner services. Personalized feeds, smart search, and recommendation engines improve usability.
- Core and Peripheral Services. Core services include messaging, social feeds, and digital wallets. Peripheral or “mini-app” services (e.g., e-commerce, ride-hailing, booking) are integrated through native development or third-party partnerships.
- In-App Ecosystems / Mini Programs. Lightweight, embedded apps (e.g., WeChat Mini Programs or Tata Neu features) that don’t require installation. Allow businesses to create services within the super app environment.
- Digital Wallets and Payment Systems. One of the most critical enablers of super apps. Support for mobile wallets, peer-to-peer transfers, crypto, and bank integration.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) and Identity Management. Users log in once and gain access to all services, with centralized authentication and role-based access control.
- Cross-Service Personalization. AI and analytics enable real-time personalization across all app modules – from shopping suggestions to financial insights.
- Offline Capabilities. Key services like transport booking or payments are optimized for low bandwidth and intermittent connectivity.
Market Drivers
Super apps are gaining traction globally due to converging economic, technological, and behavioral factors.
- App Fatigue and Demand for Simplification. Consumers are overwhelmed by the number of apps they manage. A 2024 Pew study found 65% of U.S. users prefer an all-in-one app over juggling multiple niche apps.
- Mobile-First and Digital-First Economies. In regions like Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America, many users rely solely on mobile for internet access. Super apps provide efficient low-data solutions tailored for these conditions.
- Fintech Growth and Financial Inclusion. Super apps often introduce users to digital payments, credit, insurance, and micro-investments. They are key to banking the unbanked population in emerging markets.
- Data Monetization and Cross-Service Insights. Unified apps gather more complete user data across verticals (shopping, payments, transport). This enables better predictive modeling, targeted marketing, and cross-selling.
- Strategic Ecosystem Alliances. Partnerships between telecoms, banks, retailers, and tech companies drive bundled offerings. Example: Grab integrating Mastercard, OVO, and regional SMEs.
- Public Service Integration. Governments in countries like India and UAE are exploring super apps for healthcare, ID, taxes, and e-citizen services. Stat: By 2027, the global super app market is expected to reach $720 billion, growing at a CAGR of 23.5%.

Benefits and Challenges
While the advantages of super apps are substantial, there are equally important concerns and trade-offs to address.
Key Benefits:
- Convenience & Retention. Users get a unified experience, reducing churn and boosting engagement. Sticky ecosystems keep users loyal.
- Cost-Effective Growth. Once a user is acquired for one service (e.g., food delivery), they can be cross-sold on others (e.g., insurance). Lower Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) across verticals.
- Data Integration for Insights. With a full user journey in one platform, businesses gain richer analytics. Enables hyper-personalized services, such as tailored financial offers or real-time recommendations.
- Platform Economies. Ecosystem partners (SMEs, banks, etc.) plug into the platform, creating network effects and revenue-sharing models.
- Offline/Low-bandwidth Optimization. Super apps tend to be lighter, with localized language support and offline payment options – ideal for underserved areas.
Key Challenges
- Privacy & Data Protection. Super apps collect a vast amount of personal data – raising concerns about surveillance, consent, and data breaches. Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and local regulations is essential.
- Security Risks. Centralizing user identity and financial data creates attractive attack surfaces. Requires robust encryption, multifactor authentication, and threat monitoring.
- App Bloat and Performance. Too many features can make the app sluggish and unintuitive, especially on low-end devices. Requires careful UI/UX design and modular code.
- Platform Monopoly Fears. In mature markets, regulators may resist single platforms controlling too many services (e.g., antitrust scrutiny in the EU and U.S.).
- Technical Complexity. Developing and maintaining a super app is expensive and resource-intensive. Requires cloud scalability, DevOps maturity, and agile delivery teams.

Super App Case Studies
- WeChat (China). Messaging, payments, gaming, shopping, health code. Key to China’s “zero-COVID” QR-code health infrastructure.
- Grab (SEA). Ride-hailing to food delivery to financial services. Partnered with Mastercard for regional e-wallet.
- Tata Neu (India). Integrates Tata Group brands: Air India, BigBasket, Croma. Facing adoption friction, but with huge potential.
- X (Twitter’s Transformation Attempt). Vision: Content + Payments + Messaging + Shopping. Status: Early-stage, challenges in trust and regulation.

Future Outlook: Trend or Necessity?
Is it a Trend?
- In saturated markets, super apps could become bloated and less attractive.
- Consumer trust issues in monopolized ecosystems.
- Specialized apps still win in performance and user experience.
Or a Necessity?
- In developing economies, super apps may remain essential due to infrastructure limitations.
- Businesses aiming for ecosystem dominance (e.g., fintech + e-commerce) require unified experiences.
- Gen Z and Millennials increasingly prefer holistic digital solutions.
Stat: 78% of Gen Z users globally say they are likely to use a super app if it improves everyday convenience.
Strategic Implications for Businesses
For Enterprises:
- Evaluate platform partnerships or SDKs with existing super apps.
- Embed your service within popular ecosystems (e.g., mini programs on WeChat).
- Leverage modular design to transition your own product into a super app.
For Startups:
- Focus on a core service first (e.g., payments or social) before expanding.
- Build a scalable microservices infrastructure.
- Emphasize privacy-first design to appeal to Western users.
For Governments:
- Super apps can be leveraged for public services (e.g., e-health, e-identity).
- Digital inclusion strategies must consider super app ecosystems.
- Policy must address data monopolies and user rights.
Critical Success Factors:

Conclusion
Super apps are no longer an anomaly – they represent a fundamental shift in digital interaction. Whether they remain regionally dominant or go global depends on regulatory, technical, and consumer dynamics. However, the drive toward convenience, integration, and personalization makes the super app model increasingly attractive.
For businesses, the future will likely feature hybrid models: niche apps will coexist with multi-functional platforms. But ignoring the rise of super apps could mean missing out on a massive opportunity to own more of the digital value chain.