Cybersecurity Core: How to Safeguard Data and Systems
Introduction In today’s hyper-connected world, businesses face increasing cybersecurity threats, and the importance of protecting sensitive data and systems cannot be overstat...

Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected world, businesses face increasing cybersecurity threats, and the importance of protecting sensitive data and systems cannot be overstated. As businesses adopt new technologies and rely heavily on digital infrastructure, they become vulnerable to cyberattacks that can cause serious financial and reputational damage. Therefore, building security into the core of your operations is critical to protecting both your data and systems.
This article will cover key practices and strategies to help businesses implement robust cybersecurity structures that protect against cyber threats while still complying with industry standards.
Importance of Cybersecurity
Before diving into strategies for protecting your systems, it’s important to understand why security is so important. Today, businesses deal with vast amounts of sensitive data, including customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and internal communications. Unauthorised access or breach of this data can result in:
- Data theft: Personal information, including customer data, can be stolen and used for identity theft or financial fraud.
- Business disruption: Cyberattacks, such as ransomware or distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, can shut down operations, resulting in lost productivity and revenue.
- Reputational damage: A breach can erode the trust of customers, partners, and stakeholders, which can cause long-term damage to a company’s reputation.
- Legal and financial penalties: Failure to comply with data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA can result in large fines and legal consequences.

1. Establish a Security-First Culture
The foundation of a strong cybersecurity strategy starts with the organisation’s mindset. It’s important to develop a security culture at every level of the company, ensuring that employees understand the risks and their role in mitigating them.
The key steps to creating a security culture in the first place are:
- Leadership buy-in: Security initiatives need top-down support from management to demonstrate their importance to the organisation.
- Employee training: Regular cybersecurity training ensures that employees recognize threats such as phishing, malware, and social engineering attacks.
- Clear policies and procedures: Define clear security protocols for handling sensitive data, using corporate devices, and remotely accessing systems.
2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Limiting access to sensitive data and systems to authorised personnel is a critical security measure. It minimises the potential attack surface and ensures that only those with a genuine need have access.
Best practices for access control:
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Assign access levels based on an employee’s role and responsibilities, ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to those who need it.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Requiring a combination of credentials (such as a password and a one-time code) adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorised access.
- Principle of least privilege: Limit access rights to the minimum necessary for employees to do their jobs.
![]()
3. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect sensitive data, both at rest (data at rest) and in transit (data in transit). Encryption transforms readable data into an unreadable format, ensuring that only authorised users with the correct encryption keys can access it.
Encryption Strategies:
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE): Provides encryption of data from sender to receiver, preventing interception during transmission.
- Encryption of data at rest: Sensitive data stored in databases, files, or backup systems should always be encrypted.
- Encryption key management: Implement secure key management practices to ensure that encryption keys are protected from unauthorised access.
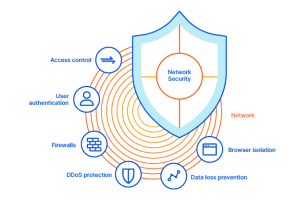
4. Deploy Network Security Measures
Network security is essential to protecting your systems from external threats. A robust network security framework prevents unauthorised access, detects suspicious activity, and responds quickly to potential attacks.
Network security best practices:
- Firewalls: A firewall acts as a first line of defence by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can automatically block potential threats.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs): Secure VPNs allow remote workers to securely access a company’s internal systems by encrypting their internet connection.
- Network segmentation: Isolate different parts of the network (for example, separating sensitive data from less important areas) to reduce the risk of widespread attacks.
5. Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Proactively identifying vulnerabilities in your systems is key to preventing cyberattacks. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing help identify weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
Audit and Assessment Strategies:
- Internal audits: Regularly review security policies, procedures, and access controls to ensure compliance and effectiveness.
- Penetration testing: Hire cybersecurity experts to conduct simulated attacks on your systems, identifying potential vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability scanning: Use automated tools to scan networks, applications, and systems for known security vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
6. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorised access to systems. Keeping your software and systems up to date with the latest patches and security updates is a simple yet highly effective measure to prevent attacks.
Patch management best practices:
- Automated updates: Automate software updates to ensure patches are applied quickly without the need for manual intervention.
- Regular patch checks: Track and review patches for third-party software, plugins, and other tools to stay up to date with vulnerabilities.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities: Stay up to date with new zero-day vulnerabilities and work with your vendors to patch critical systems immediately.
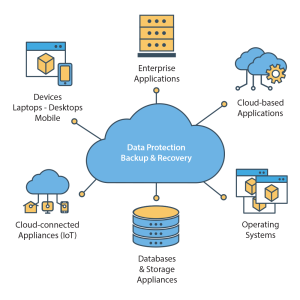
7. Implement Data Backup and Recovery Solutions
Even with robust security measures in place, breaches and data loss can still happen. A robust data backup and recovery plan ensures that critical data can be recovered in the event of an attack, hardware failure, or human error.
Backup Strategies:
- Regular backups: Perform daily or weekly backups of critical data and store backups in a secure off-site location.
- Redundant storage: Use redundant storage solutions (such as cloud storage or on-premises NAS) to ensure that data is not lost in the event of hardware failure.
- Disaster recovery plan: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps to restore data and resume business operations after an incident.
8. Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Different industries have specific regulations governing data security. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in large fines and lawsuits, so it is important to stay up to date with the latest data protection laws.
The main regulatory frameworks are:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): regulates the collection, processing, and storage of personal data for businesses operating in the European Union.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): protects sensitive patient health information for healthcare providers in the United States.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): sets security requirements for businesses that process payment card data.
9. Monitor and Respond to Threats in Real-Time
Advanced threats can emerge at any time, and having real-time monitoring systems in place allows companies to detect and respond to incidents before they escalate.
Best practices for threat detection and response:
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems: Use SIEM tools to aggregate and analyse security alerts across the organisation, allowing you to quickly detect suspicious activity.
- Incident response plan: Develop a structured incident response plan that outlines how your team should respond to different types of cyberattacks.
- Continuous monitoring: Implement 24/7 monitoring of critical systems and data to detect anomalies and threats as they occur.

Conclusion
Securing data and systems is an ongoing process that requires a comprehensive approach. By embedding security at the core of their operations – from developing a security-first culture to implementing advanced encryption, access controls, and real-time threat detection – enterprises can reduce risk and protect themselves from the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape.
As the digital world continues to grow, so do the threats against it. Companies that prioritise and continually improve their security strategies will not only protect their data, but also earn the trust of their customers, partners, and employees. Security is not just a technical challenge, but a business imperative that must be woven into the fabric of every organisation.